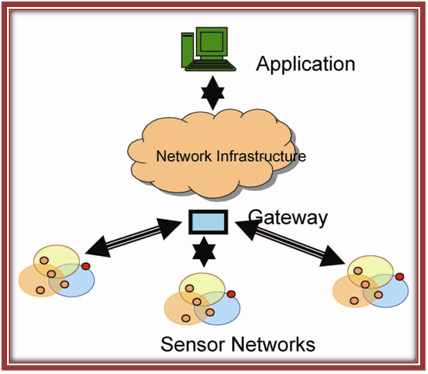
NS3 for WSN is also a collection of nodes organize into a cooperative network.Each node consists of processing capability, may also contain multiple types of memory, have also a RF transceiver, have a power source, and accommodate various sensors and also actuators.Ns3 WSN system incorporates a gateway that also provides wireless connectivity back to the wired world and distributed nodes. The wireless protocol you also select depends also on your application requirements.
Applications of WSN (Wireless Sensor Network):
- Asset tracking.
- Periodic measurements.
- Environmental and monitoring of air, water and also soil.
- Event detection.
- Process monitoring.
- Industrial machine monitoring.
- Structural monitoring also for buildings and bridges.
Components of WSN node:
- Sensor interface.
- Radio.
- Analog circuit.
- Battery.
- Microcontroller etc.
Need for introducing WSN:
- Production cost.
- Fault tolerance.
- Security.
- Lifetime.
- Scalability.
- Real time.
Architecture of NS3 for WSN:
Sample code for WSN:
double DegreesToRadians (double degrees)
{
return degrees * M_PI / 180.0;
}
double RadiansToDegrees (double radians)
{
return radians * 180.0 / M_PI;
}
std::ostream& operator<< (std::ostream& os, const Angles& a)
{
os << "(" << a.phi << ", " << a.theta << ")";
return os;
}
std::istream &operator >> (std::istream &is, Angles &a)
{
char c;
is >> a.phi >> c >> a.theta;
if (c != ':')
{
is.setstate (std::ios_base::failbit);
}
return is;
}
Angles::Angles ()
: phi (0),
theta (0)
{
}
Angles::Angles (double p, double t)
: phi (p),
theta (t)
{
}
Angles::Angles (Vector v)
: phi (std::atan2 (v.y, v.x)),
theta (std::acos (v.z / sqrt (v.x*v.x + v.y*v.y + v.z*v.z)))
{
}
Angles::Angles (Vector v, Vector o)
: phi (std::atan2 (v.y - o.y, v.x - o.x)),
theta (std::acos ((v.z - o.z) / CalculateDistance (v, o)))
{
}