NS3 Manet Simulation, the routers are free to move randomly and organize themselves arbitrarily. Thus, the network’s wireless topology may change rapidly and unproductively.An ad hoc network is a collection of mobile nodes that dynamically form a temporary network and are capable of communicating with each other without the use of a network infrastructure or any centralized administration.We Provide customized NS3 MANET SIMULATION Projects for Students and Research Scholars based on your requirement and 100% satisfaction.
Features of MANET:
- Energy constraint are of important consideration.
- Security is limited.
- Autonomous and no infrastructure needed.
- Communication is via wireless means.
- Can be setup anywhere.
- Nodes can perform the roles of both hosts and routers.
- Dynamic network topology and also frequent network updates.
- No centralized controller and infrastructure. Intrinsic mutual trust.
Broadcasting approaches in MANET:
- Geocasting.
- Unicasting.
- Broadcasting.
- Multicasting.
Challenges on routing:
- Location-aided routing.
- Routing.
- Achieve QoS.
- Communication within an ad hoc network, inter-networking between MANET and fixed networks.
- Power consumption.
- Security and reliability.
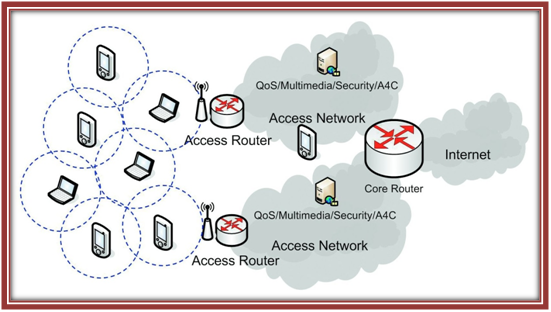
Architecture of MANET:
Sample code for MANET:
CommandLine cmd;
cmd.Parse (argc, argv);
NodeContainer c;
c.Create (100);
MobilityHelper mobility;
mobility.SetPositionAllocator ("ns3::RandomDiscPositionAllocator",
"X", StringValue ("100.0"),
"Y", StringValue ("100.0"),
"Rho", StringValue ("ns3::UniformRandomVariable[Min=0|Max=30]"));
mobility.SetMobilityModel ("ns3::RandomWalk2dMobilityModel",
"Mode", StringValue ("Time"),
"Time", StringValue ("2s"),
"Speed", StringValue ("ns3::ConstantRandomVariable[Constant=1.0]"),
"Bounds", StringValue ("0|200|0|200"));
mobility.InstallAll ();
Config::Connect ("/NodeList/*/$ns3::MobilityModel/CourseChange",
MakeCallback (&CourseChange));
[/et_pb_text][/et_pb_column][/et_pb_row][/et_pb_section]